

Testosterone and Your Athletic Performance: How It Affects Strength and Recovery
09.06.2025Strength, endurance, recovery — every athlete knows how crucial these three elements are. But did you know that testosterone plays a key role in achieving them? This hormone is your ally in building fitness and pushing beyond your limits. How can you support it naturally? Why should you consider the Tribulus+Shilajit supplement? Discover how to improve your athletic results and take care of your body!
What is Testosterone?
Testosterone is a sex hormone most commonly associated with men, though it also plays a significant role in women’s bodies. In women, levels range from 0.7 to 2.8 nmol/l, while in adult men they typically range from 7.7 to 29.4 nmol/l. It is responsible for the development of sexual characteristics, affects libido, and influences overall well-being and metabolic health. Both excess and deficiency can cause problems — high levels may contribute to hair loss, while low levels can lower libido and cause muscle weakness.
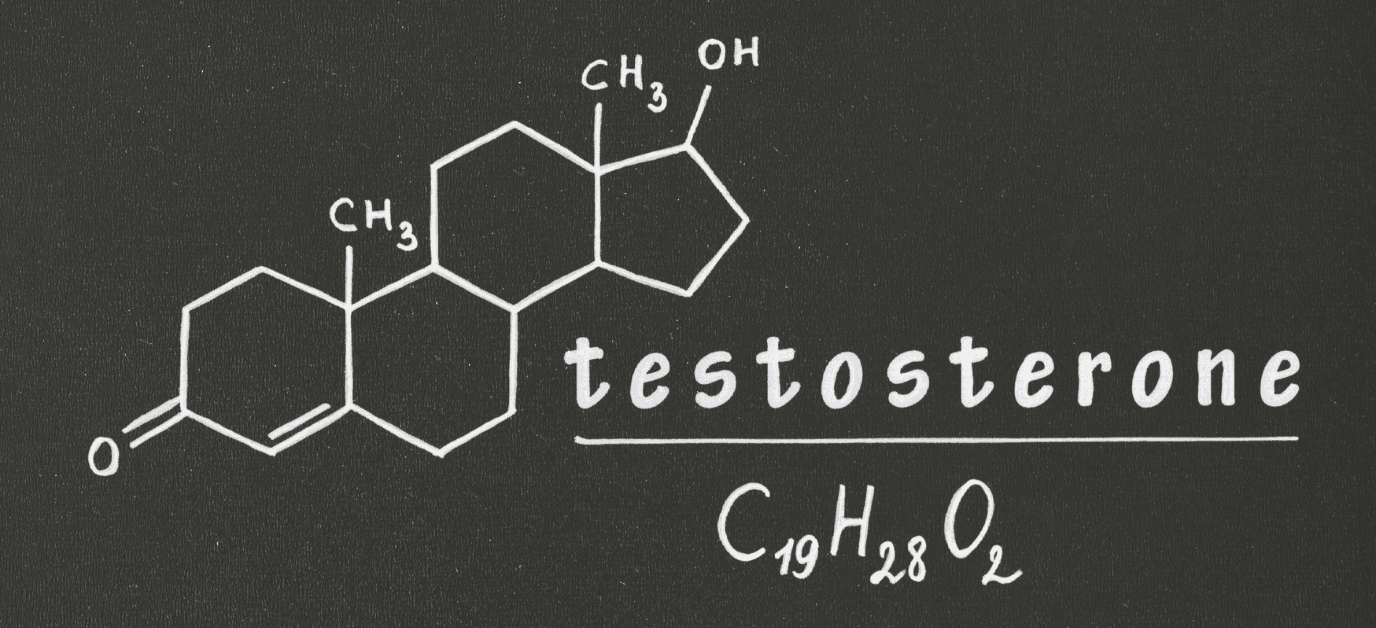
What Role Does Testosterone Play in Sports?
Testosterone is much more than a sex hormone — it’s a true “power engine” for athletes of both sexes. It supports muscle mass, strength, energy, and recovery, which allows you to train at your peak. Thanks to this hormone, your body can handle increasing training demands, enabling you to achieve goals that once seemed out of reach.
1. Strength and Muscle Development
Testosterone has an anabolic effect — it stimulates protein synthesis in muscles, promoting growth and greater strength [. It helps your body build a muscular "armor," allowing you to lift more in the gym or break records in other disciplines. Low testosterone levels result in less effective training and slower muscle gains.

2. Faster Recovery
As you know, after intense training, the body needs time to recover. Here again, testosterone plays a vital role by supporting the repair of damaged muscle fibers [. Acting like a “mechanic,” the higher your testosterone level, the faster you bounce back after physical exertion.
3. Energy and Endurance
Testosterone supports energy metabolism, helping the body use fat more efficiently as a fuel source. It also boosts red blood cell production, which improves muscle oxygenation during exercise [. The result? Greater endurance and energy, helping you perform at your best in training and competition.

4. Reduced Body Fat
Higher testosterone levels help maintain lower body fat [. This not only improves body composition but also enhances strength-to-weight ratio — a crucial factor in many sports disciplines, from running to martial arts.
5. Motivation and Competitiveness
It’s no coincidence that testosterone is called the “hormone of winners.” It influences confidence, determination, and risk-taking — all key to thriving in competitive environments [. On the flip side, excessive levels can lead to uncontrolled aggression, which is why maintaining a healthy balance is essential.

What Happens with Low Testosterone Levels?
Low testosterone can seriously hinder your athletic progress. It means less strength, slower recovery, and lower energy. Over time, concentration difficulties and mood disturbances may also arise — factors that directly impact performance.
How to Naturally Boost Testosterone Levels
Many factors influence testosterone levels, including age, lifestyle, and diet. Sleep is absolutely fundamental — during nighttime rest, the body regenerates and produces hormones like testosterone [. Nutrition and exercise are the next pillars of support. Regular strength training, especially with resistance, is a natural way to stimulate testosterone production [.
Additionally, include foods rich in zinc (e.g., pumpkin seeds, oysters), selenium (Brazil nuts, tuna), and boron (almonds, raisins), along with magnesium (spinach, nuts) and vitamin D (fish, eggs). If, despite a healthy lifestyle, you still feel lacking, well-chosen supplementation — such as Tribulus+Shilajit — can be a valuable aid, helping correct deficiencies and supporting your athletic goals.
Tribulus+Shilajit — Why Choose This Natural Testosterone Booster?
Tribulus+Shilajit is a supplement designed for those looking to naturally support testosterone levels and enhance physical performance. Its formula contains zinc, which helps maintain normal testosterone levels in the blood and supports normal fertility and reproductive function. Additionally, zinc and selenium jointly support the proper functioning of the immune system and protect cells from oxidative stress [.
The supplement also features an extract of Tribulus terrestris fruit, standardized to 90% saponins — a plant valued in Eastern traditions, particularly in China and India. Another key ingredient is shilajit, also known as mumijo — a natural substance from the Himalayas formed over centuries from plant decomposition and microbial activity. This unique “Himalayan gift of nature” contains 60% fulvic acids and 12% humic acids. The formula is further enhanced with L-arginine, an amino acid precursor to nitric oxide that supports blood circulation, and boron — an important trace mineral.
The recommended dose of Tribulus+Shilajit is 2 capsules per day, taken with a meal and a glass of water. This provides:
200 mg of Tribulus terrestris extract, standardized to 90% saponins, delivering 180 mg of saponins and equivalent to 4,000 mg of raw fruit used to prepare the extract.
200 mg of shilajit extract (DER 60:1), equivalent to 12,000 mg of raw Himalayan material.
10 mg of zinc, supporting normal testosterone levels in the blood.
55 µg of selenium,
3 mg of boron,
700 mg of L-arginine.
[1] Bhasin S, Brito JP, Cunningham GR, Hayes FJ, Hodis HN, Matsumoto AM, Snyder PJ, Swerdloff RS, Wu FC, Yialamas MA. Testosterone Therapy in Men With Hypogonadism: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018 May 1;103(5):1715-1744. doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-00229. PMID: 29562364.
[2] Antonio, J., Uelmen, J., Rodriguez, R., & Earnest, C. (2000). The effects of Tribulus terrestris on body composition and exercise performance in resistance-trained males. International journal of sport nutrition and exercise metabolism, 10(2), 208–215. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.10.2.208
[3] Kraemer WJ, Ratamess NA. Hormonal responses and adaptations to resistance exercise and training. Sports Med. 2005;35(4):339-61. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200535040-00004. PMID: 15831061.
[4] Saad F, Gooren L. The role of testosterone in the metabolic syndrome: a review. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2009 Mar;114(1-2):40-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2008.12.022. PMID: 19444934.
[5] Grossmann M, Zajac JD. Management of side effects of androgen deprivation therapy. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2011 Sep;40(3):655-71, x. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2011.05.004. PMID: 21889727.
[6] Carré JM, Olmstead NA. Social neuroendocrinology of human aggression: examining the role of competition-induced testosterone dynamics. Neuroscience. 2015 Feb 12;286:171-86. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.11.029. Epub 2014 Nov 26. PMID: 25463514.
[7] Van Cauter E, Holmback U, Knutson K, Leproult R, Miller A, Nedeltcheva A, Pannain S, Penev P, Tasali E, Spiegel K. Impact of sleep and sleep loss on neuroendocrine and metabolic function. Horm Res. 2007;67 Suppl 1:2-9. doi: 10.1159/000097543. Epub 2007 Feb 15. PMID: 17308390.
[8] Prasad AS. Clinical, immunological, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant roles of zinc. Exp Gerontol. 2008 May;43(5):370-7. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2007.10.013. Epub 2007 Nov 1. PMID: 18054190.


